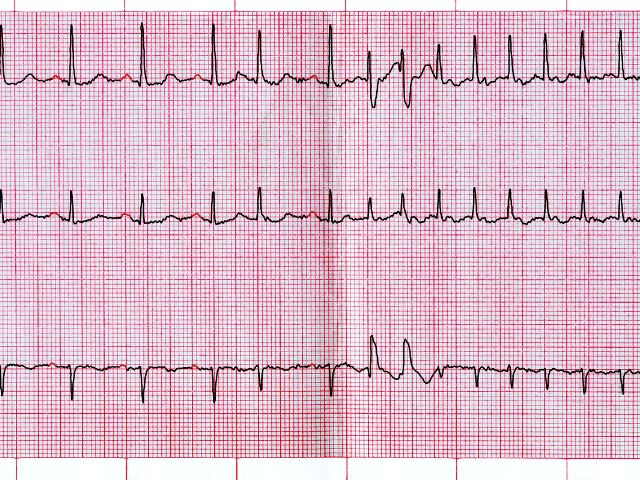
In the United States, those over the age of sixty-five are at risk of developing atrial fibrillation because of cardiovascular aging and it is the most frequent significant arrhythmia.
Atrial fibrillation or AFib is a serious heart condition that disrupts the electrical signals in the heart, causing an irregular heartbeat and higher association of devastating strokes. If left untreated, AFib can lead to heart failure, blood clots in the heart, chest pain, and can lead to sudden cardiac death.
High blood pressure, valvular heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and sleep apnea can increase a patient’s risk of AFib. Lifestyle contributors include alcohol, caffeine, dehydration, poor sleep patterns, and stress.
In addition, stress can cause changes in the electrical repolarization of cells, evoked potentials, and increase in T-wave amplitude, promoting cardiac arrhythmogenesis.