What Skills Does a Nursing Assistant Need?
A nursing assistant is bound by the scope of practice in their state’s Board of Nursing, which can vary slightly from state to state. Each state controls the skills a nursing assistant may perform and holds them to a standard of practice. For example, in some states, a nursing assistant is able to help administer tube feedings but in other states that is not allowed. Some states allow the certified nursing assistant (CNA) to administer limited medications, whereas other states do not allow any medications to be given by the CNA.
Nursing assistants receive training in a variety of skills to prepare them for their role in providing direct patient care. Some of the key skills that nursing assistants typically receive training in include:
Patient Care Skills: Nursing assistants are trained in providing basic care and assistance to patients, including bathing, dressing, grooming, and oral hygiene. They learn techniques for safe and efficient transfer and positioning of patients, as well as assisting with activities of daily living (ADLs).
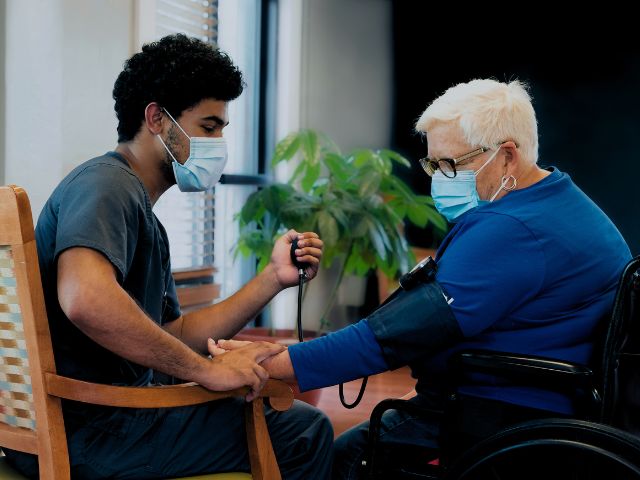
Vital Signs Measurement: Nursing assistants are trained to measure and record vital signs, such as blood pressure, pulse rate, temperature, and respiration rate. They learn proper techniques for using various equipment and instruments to obtain accurate readings.
Infection Control: Nursing assistants receive training in infection control measures to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare settings. They learn about hand hygiene, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and the importance of maintaining a clean and safe environment.
Basic Medical Procedures: Nursing assistants may receive training in performing basic medical procedures under the supervision of licensed nurses. This may include dressing changes, applying topical medications, collecting specimens for testing, and assisting with medical equipment and devices.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Nursing assistants learn effective communication techniques to interact with patients, their families, and the healthcare team. They develop skills in active listening, empathy, and maintaining patient confidentiality.
Safety and Emergency Procedures: Nursing assistants are trained in recognizing and responding to emergencies, such as falls, cardiac arrest, and choking. They learn how to initiate basic life support (CPR) and first aid techniques and follow facility-specific safety protocols.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Nursing assistants are taught how to accurately document patient care activities, observations, and vital signs in medical records. They learn about the importance of maintaining confidentiality and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines.
Additionally, nursing assistants may receive training in specialized areas such as dementia care, end-of-life care, and specific procedures or protocols specific to the healthcare facility or population they will be serving. It’s worth noting that the specific skills and training requirements can vary depending on the country, state, or region where a nursing assistant is practicing. Training programs and curriculum may be regulated and governed by local healthcare authorities or licensing bodies to ensure the competency and quality of nursing assistants.