Radiological Findings of Subdural Hematoma
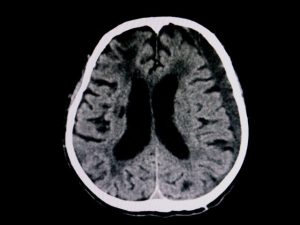
After the initial exam, the primary nurse transports to patient to the CT scanner. The CT scan of the head and neck shows a simple subdural hematoma without parenchymal contusion and a small region of active hemorrhage in the posterior region. There is no midline shift.
Because of her fall, your patient has suffered a traumatic brain injury (TBI), a minor skull fracture, and a subdural hematoma.
After a consult with neurosurgery, it is determined that the patient will not require surgical intervention. The neurosurgery service admits the patient for observation.
During the patient’s hospital stay the patient receives anticonvulsants to prevent seizures, and a repeated CT scan to monitor the hematoma.
The second CT, six hours later, showed a notable reduction of the hematoma and with improving neurological function.